Using the switch selection statement to simplify conditional statements blocks
A beginner guide to programming with .NET 5 and C#

This article explores how to simplify certain complex conditional blocks by introducing the switch statement.
The switch keyword is very standard in programming languages.
We use it to compare a variable with many values.
Please note that we are not covering switch expressions in this article.
This article is part of a learn programming series where you need no prior knowledge of programming. If you want to learn how to program and want to learn it using .NET/C#, this is the right place. I suggest reading the whole series in order, starting with Creating your first .NET/C# program, but that’s not mandatory.
This article is part of a sub-series, starting with Introduction to Boolean algebra and logical operators. It is not mandatory to read all articles in order, but I strongly recommend it, especially if you are a beginner. If you are already reading the whole series in order, please discard this word of advice.
The Switch
In the previous article, Using if-else selection statements to write conditional code blocks, we covered the basics behind contextual code.
This article explores the switch statement by converting a complex if block to a switch.
We go through the syntax afterward.
Initial code (if):
using System;
Console.WriteLine("Enter something: ");
var input = Console.ReadLine();
if (input == "hello" || input == "world" || input == "hello world")
{
Console.WriteLine("Hello World!");
}
else if (input == "goodbye")
{
Console.WriteLine("Au revoir!"); // Goodbye in French
}
else if (input == "name?")
{
Console.WriteLine("What is your name?");
var name = Console.ReadLine();
Console.WriteLine($"Your name is {name}");
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine("Invalid input");
}
Console.WriteLine("End of the program.");
Converted code (switch):
using System;
Console.WriteLine("Enter something: ");
var input = Console.ReadLine();
switch (input)
{
case "hello":
case "world":
case "hello world":
Console.WriteLine("Hello World!");
break;
case "goodbye":
Console.WriteLine("Au revoir!"); // Goodbye in French
break;
case "name?":
Console.WriteLine("What is your name?");
var name = Console.ReadLine();
Console.WriteLine($"Your name is {name}");
break;
default:
Console.WriteLine("Invalid input");
break;
}
Console.WriteLine("End of the program.");
Let’s now analyze the previous code, starting with the new keywords:
switchcasebreakdefault
The switch keyword starts a code block that must be followed by a variable in parenthesis, like this:
switch (variable)
{
// Code block
}
The case keyword, followed by a value and :, is an equality comparison against the original variable passed to the switch.
You can see case "goodbye": as the equivalent of if (variable == "goodbye").
A case block can be empty or end with a break or return.
We will not cover the return keyword in this article because it is related to other concepts that we have not explored yet.
When the case is empty, it continues to the next case.
For example, case "hello": falls back to case "world": that falls back to case "hello world": that gets executed.
Interesting fact: C# does not support falling from one non-empty
caseto another as some other languages do.
The break keyword is a jump statement that allows controlling the flow of the program by exiting the current block, a.k.a. jumping out of the switch block.
Finally, in a switch block, the default keyword is the equivalent of the else; it is hit when no other case was hit.
Before the exercise, let’s peek at the program flow created by a switch statement.
Flow of the program
In a nutshell, a switch statement allows comparing if a variable is equal to a value from a list of cases.
Here is a visual representation of the program flow created by a switch block:
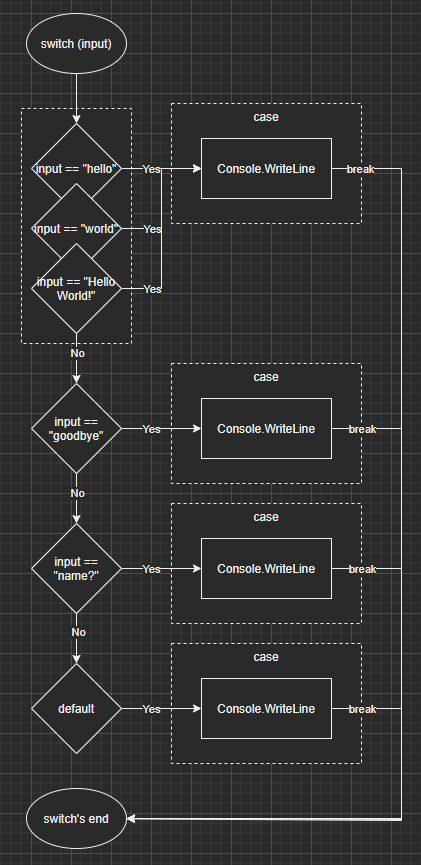
Next, it’s your turn to try it out.
Exercise
Convert the following code to use a switch statement.
var input = Console.ReadLine();
if(input == "A")
{
Console.WriteLine("1");
}
else if (input == "B")
{
Console.WriteLine("2");
}
else if (input == "C")
{
Console.WriteLine("3");
}
else if (input == "D")
{
Console.WriteLine("4");
}
else if (input == "E")
{
Console.WriteLine("5");
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine("Invalid input");
}
Once you are done, you can compare with My Solution below.
My Solution
Program.cs
var input = Console.ReadLine();
switch (input)
{
case "A":
Console.WriteLine("1");
break;
case "B":
Console.WriteLine("2");
break;
case "C":
Console.WriteLine("3");
break;
case "D":
Console.WriteLine("4");
break;
case "E":
Console.WriteLine("5");
break;
default:
Console.WriteLine("Invalid input");
break;
}
Good job! You completed another small chapter of your programming journey.
Conclusion
This article explored the switch statement, which allows comparing if a variable is equal to a value from a list of cases.
The switch statement is another way to create conditional code and control our programs’ flow.
The switch statement is handy for variables with a finite number of values like enums.
More recent versions of C# also introduce switch expressions and pattern matching that open many other possibilities. However, many of those possibilities require knowledge of object-oriented programming that we are not exploring in this article series.
Please leave your questions or comments below or drop me a Tweet.
Next step
It is now time to move to the next article: Boolean algebra laws.
Table of content
Now that you are done with this article, please look at the series’ content.
| Articles in this series |
|---|
|
Creating your first .NET/C# program
In this article, we are creating a small console application using the .NET CLI to get started with .NET 5+ and C#.
|
|
Introduction to C# variables
In this article, we explore variables. What they are, how to create them, and how to use them. Variables are essential elements of a program, making it dynamic.
|
|
Introduction to C# constants
In this article, we explore constants. A constant is a special kind of variable.
|
|
Introduction to C# comments
In this article, we explore single-line and multiline comments.
|
|
How to read user inputs from a console
In this article, we explore how to retrieve simple user inputs from the console. This will help us make our programs more dynamic by interacting with the user.
|
|
Introduction to string concatenation
In this article, we dig deeper into strings and explore string concatenation.
|
|
Introduction to string interpolation
In this article, we explore string interpolation as another way to compose a string.
|
|
Escaping characters in C# strings
In this article, we explore how to escape characters like quotes and how to write special character like tabs and new lines.
|
|
Introduction to Boolean algebra and logical operators
This article introduces the mathematical branch of algebra that evaluates the value of a condition to true or false.
|
|
Using if-else selection statements to write conditional code blocks
In this article, we explore how to write conditional code using Boolean algebra.
|
|
Using the switch selection statement to simplify conditional statements blocks
You are here
In this article, we explore how to simplify certain conditional blocks by introducing the switch statement.
|
|
Boolean algebra laws
This article explores multiple Boolean algebra laws in a programmer-oriented way, leaving the mathematic notation aside.
|
|
This is the end of this series
This article series was migrated to a newest version of .NET. Have a look at the .NET 6 series for more!
|